Imagine Math different.
Learning List says, “MathImagine is 95% Aligned!”
We begin with the Math Standards and then Build our Math Curriculum
This helps ensure student learning is targeted to the tasks they’ll be expected to know in their math classes and on state assessments. Our products are great for everyone…Students, Parents, Teachers, & Administrators

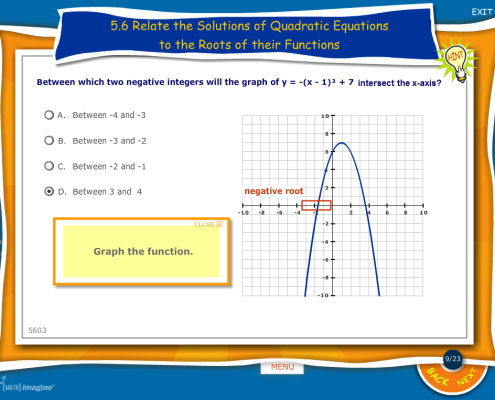
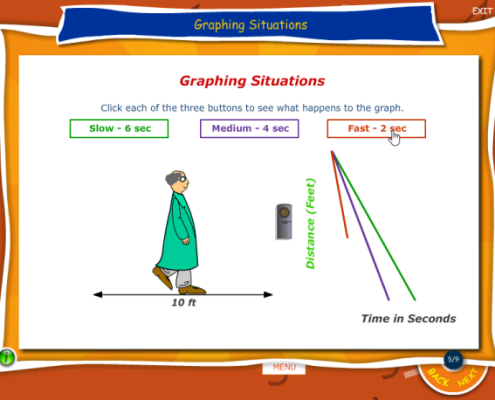
 Problem Solving Approach throughout Lessons and Quizzes
Problem Solving Approach throughout Lessons and Quizzes
Students learn math concepts through interactive and engaging lessons, always focusing on a problem-solving approach. They’re are also presented with practice questions assessment, targeting each math standard objectives! The quiz items are pulled from a database of thousands of questions.
- When they miss a question or respond incorrectly during a lesson, feedback is immediate, animated and thought provoking.
- Not just a written textbook explanation of how to solve the problem. Content is developed to nurture problem solvers, as opposed to students who memorize procedures that are soon forgotten.
Compare MathImagine’s™ problem-solving approach with other programs. Experience our student-friendly interactive lessons
 Increases Math Vocabulary & Academic Language for ALL Students, Including English Learners and Struggling Students
Increases Math Vocabulary & Academic Language for ALL Students, Including English Learners and Struggling Students
Students learn the academic language alongside building their math conceptual understanding. Our lessons and quizzes USE the mathematics vocabulary and academic language. Math vocabulary is animated and helps students visualize math vocabulary throughout lessons and quizzes. This is one of many reasons school districts with large populations of English Learners and at-risk students use our program!
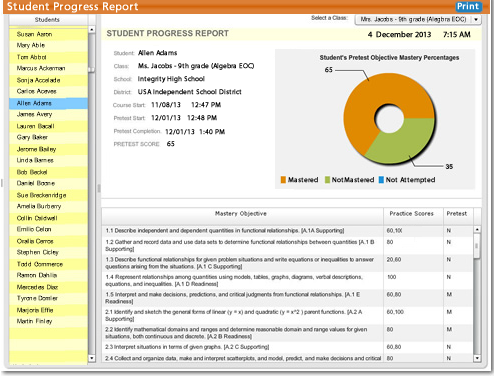
 Multi-level Robust Reporting
Multi-level Robust Reporting
Districts, Campuses, Teachers, Parents, and Students are able to make in-time instructional decisions, focus learning and make informed decisions that are on target using MathImagine’s™ unique reporting system.
 Backed by over 20 Years of Experience in Creating Products for ALL Students
Backed by over 20 Years of Experience in Creating Products for ALL Students
We’re not new to creating programs that create success for ALL students, including English learners and struggling learners. We have the experience and implementation knowledge that goes beyond any other product on the market. MathImagine™ is designed and built by Teachers and Curriculum experts from across the United States using best teaching practices with the whole child in mind. We encourage you to compare our lessons, quizzes, and reports to other programs!
Contact us to get a quote for your online subscription to MathImagine™ from L&M Instructional Services, 210.492.2783, info@lmmath.com.
______


















Follow Us